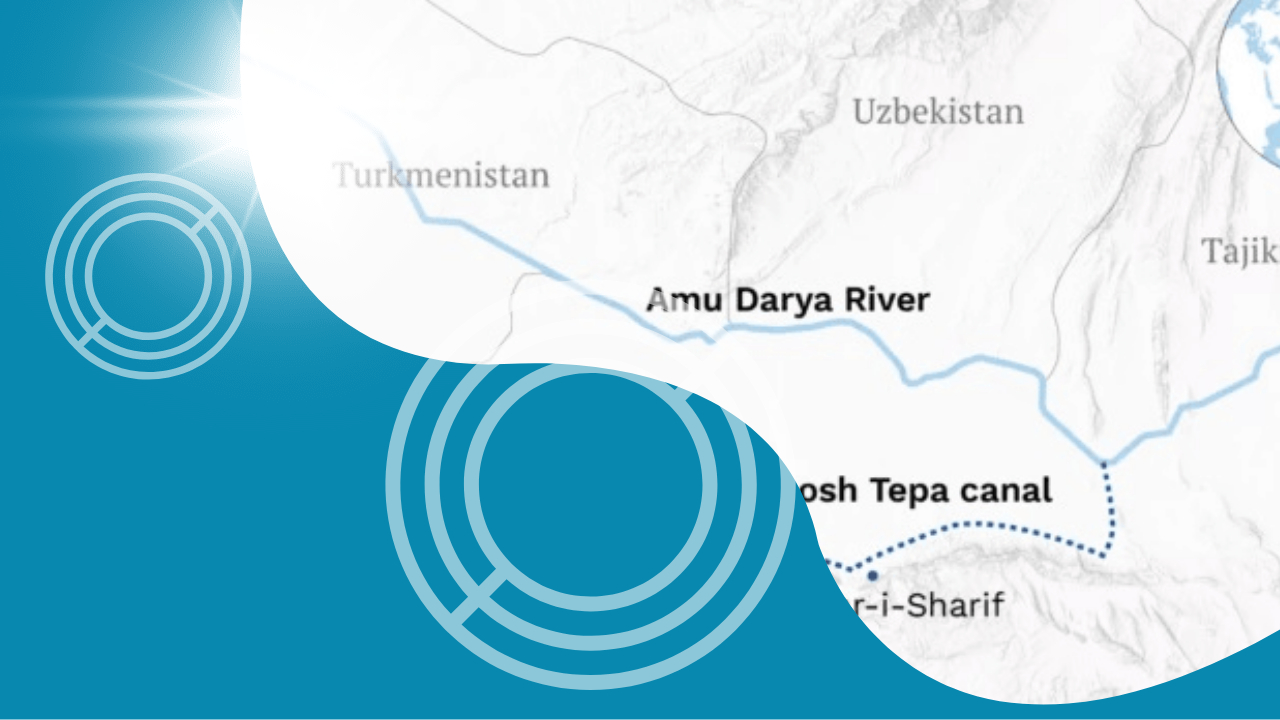
The construction of the Qosh Tepa Canal in Afghanistan is poised to have significant implications for economic development and the mining industry in Central Asia. The canal, intended to irrigate vast areas of arid land, has sparked concerns and discussions among neighbouring countries like Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan due to its potential impact on water resources and agricultural production.
Economic Development:
- Water Woes: Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan are currently facing severe water shortages, with projections indicating a significant deficit by 2030. The canal’s diversion of water from the Amu Darya River could exacerbate these shortages, affecting agricultural productivity in both countries.
- Agricultural Impact: Given that Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan heavily rely on agriculture, any decline in water flow due to the canal could lead to increased salinisation and reduced agricultural output, impacting their economies.
- Regional Cooperation: The construction of the canal highlights the need for new agreements on water management between Afghanistan and its Central Asian neighbours to foster regional cooperation in sustainable water management.
Mining Industry:
- Chinese Investment: The Taliban government announced a significant investment by a Chinese mining company in Afghanistan, aiming to mine resources and develop infrastructure. This investment could potentially impact the mining landscape in the region.
- Economic Crisis Alleviation: Discussions among key regional players like China, Russia, Pakistan, and Iran indicate a broader interest in addressing Afghanistan’s economic crisis, which could influence mining activities and economic dynamics in Central Asia.
While the construction of the Qosh Tepa Canal presents opportunities for agricultural development in Afghanistan, it also raises concerns about water scarcity and economic repercussions for neighbouring countries. The influx of investments into Afghanistan’s mining sector adds another layer of complexity to the economic landscape of Central Asia, emphasising the interconnectedness of regional economies and the importance of sustainable resource management agreements.